In a previous post, I’d covered how to use Kube-cert-manager to automatically create and update TLS certificates from LetsEncrypt.org.
Kube-cert-manager was, even then, not seeing a lot of activity and Jetstack’s cert-manager was the project to watch/follow. Given that it was still early days with cert-manager, I used Kube-cert-manager. In the last 6 months, cert-manager has moved quite a bit forward. Also, LetsEncrypt now supports wildcard certificates.
Today, I decided to give it a spin and was pleasantly surprised. If you need to, you can use both kube-cert-manager and cert-manager at the same time - though there’s no reason to do that.
- But why should you move?
-
-
Kube-cert-managerhas a big fat deprecation notice on their website. -
cert-managersupports ACME v2 - this means that LetsEncrypt’s recent support for wildcard subdomain is usable. You can just get one wildcard cert and be done with it.
-
- Okay - let’s move already!
-
-
Install
cert-managerwith Helm-
Update helm repo -
helm repo update -
Install - `helm install --name cert-manager --namespace kube-system --set rbac.create=false stable/cert-manager `
-
note the
--set rbac.create=falseabove. Include that only if your cluster does not use RBAC
-
-
-
- Create an
issuerresource -
> cat letsencrypt-prod.yaml apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: Issuer metadata: name: letsencrypt namespace: default spec: acme: server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory email: xxxxxx@xxxx # Name of a secret used to store the ACME account private key privateKeySecretRef: name: letsencrypt # ACME DNS-01 provider configurations dns01: # Here we define a list of DNS-01 providers that can solve DNS challenges providers: - name: cf-dns cloudflare: email: xxxx@xxxx # A secretKeyRef to a cloudflare api key apiKeySecretRef: name: cloudflare-apikey key: CLOUDFLARE_API_KEY # modify with your email; also configure the DNS-01 provider. # If you need to use one of the other providers, they are documented here - # https://cert-manager.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/issuers/acme/dns01.html#supported-dns01-providers > kubectl apply -f letsencrypt-prod.yaml > kubectl describe issuer letsencrypt ... ... Conditions: Last Transition Time: 2018-07-05T05:52:05Z Message: The ACME account was registered with the ACME server Reason: ACMEAccountRegistered Status: True Type: Ready Events: <none> - Create a
certificateresource -
> cat certificate-rraghur.in.yaml apiVersion: certmanager.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: Certificate metadata: name: rraghur-in namespace: default spec: secretName: rraghur-in-tls issuerRef: name: letsencrypt commonName: '*.rraghur.in' acme: config: - dns01: provider: cf-dns domains: - '*.rraghur.in' > kubectl apply -f certificate-rraghur.in.yaml certificate "rraghur-in" created > kubectl describe certificates.certmanager.k8s.io rraghur-in Name: rraghur-in Namespace: default ... ... ... Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal CreateOrder 1m cert-manager Created new ACME order, attempting validation... Normal DomainVerified 20s cert-manager Domain "rraghur.in" verified with "dns-01" validation Normal IssueCert 18s cert-manager Issuing certificate... Normal CertObtained 17s cert-manager Obtained certificate from ACME server Normal CertIssued 17s cert-manager Certificate issued successfully - Apply the cert to your ingress resource
-
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Ingress metadata: annotations: nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: "3600" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: "3600" labels: app: jenkins name: jenkins-ingress namespace: default spec: rules: - host: jenkins.rraghur.in http: paths: - backend: serviceName: jenkins-jenkins servicePort: 8080 path: / tls: - hosts: - jenkins.rraghur.in secretName: rraghur-in-tls - End result
-
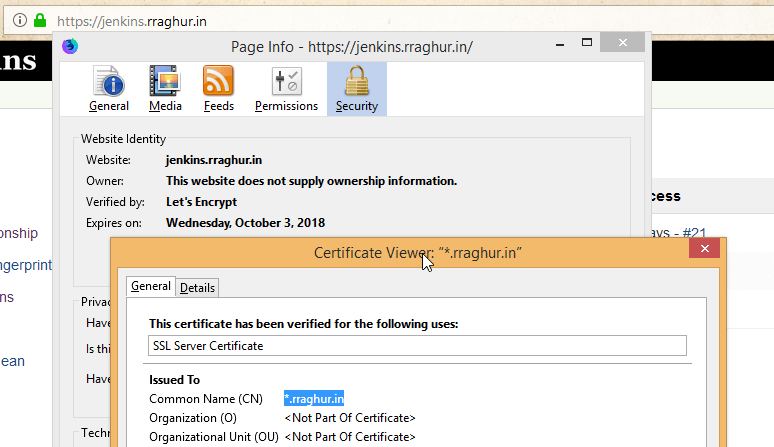
cert-manager will also watch all certs it has created and auto renew them when they near expiry. You can also have cert-manager watch ingress resources and generate certs automatically based on annotations.